Print 2 Mould. Why choose this method over conventional tool injection moulding and 3D printing?
Today, people are very demanding in their needs and wants. Whether it be more time, lower costs, quicker delivery, there is a continuous demand for compromise, whilst still maintaining quality and performance. Having options allows for the best result from the most appropriate process and when it comes to injection moulding methods, it is no different. There are various types of injection moulding and tool manufacture, weighing up the most suitable option is crucial.
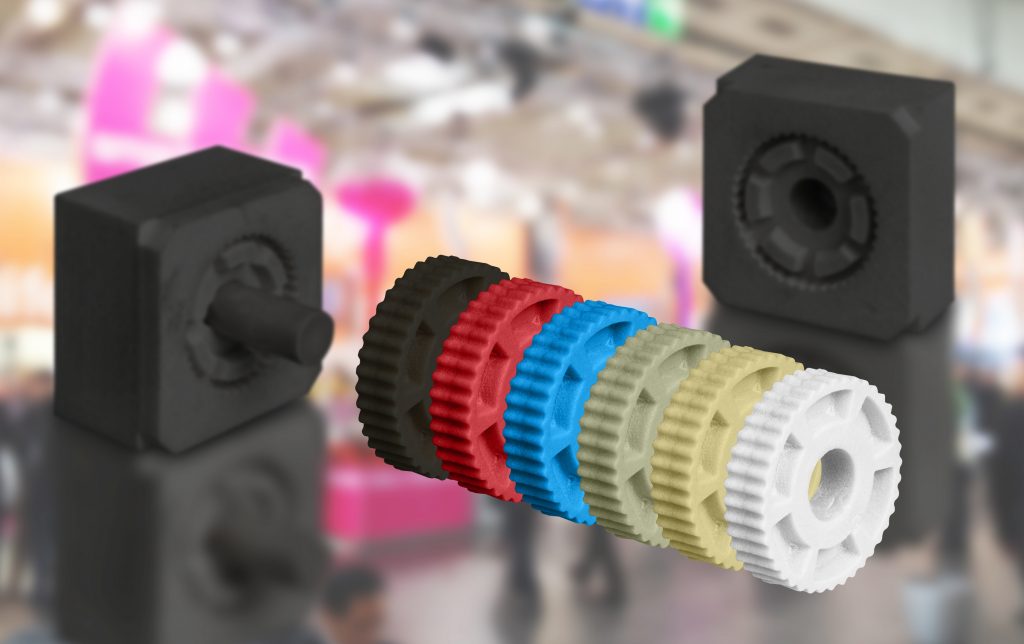
igus® already exploits the various platforms of tool manufacturing; from the more traditional hard tool to 3D printed tools, from rapid injection moulding using Aluminium tools to 3D printed parts. There are obvious advantages with all methods but there are times when printed moulds make more sense.
What is a P2M tool and why choose this over traditional injection mould tools?
P2M is what igus® refer to as our print to mould service, this is where we 3D print a tool and then inject one of our materials into it. This combines both injection moulding and 3D printing methods to create specific parts. This is ideal for pre-production and/or low volume parts as these are manufactured effectively and at a low cost. This method can cost up to 80% LESS than the hard tool process. The result is an igus® produced part in an igus® material with the option to replicate this if there were higher volume demands within a hard steel tool. Therefore, we have the option to utilise any one of the 50 material available from igus®. Quicker delivery- The traditional hard tooling method has a lead time of up to 12 weeks for the tool and samples to be produced. P2M tools can be made and parts produced in a little over a week.

We have recently launched an online tool for P2M, which allows you to add a file into the website and have a price calculated for both the tool and the parts in an instant.
3D printing over P2M?
We discussed speed in comparison to P2M versus traditional moulded parts being produced, but this goes one step further when analysing pros and cons of P2M versus 3D printing. 3D printed parts can be produced in 24 hours, depending on the part. 24 hours! With delivery coming from our manufacturing base in Cologne, Germany, the maximum lead time is appox 7 working days from date of order to receipt of parts, which is quicker than P2M parts.
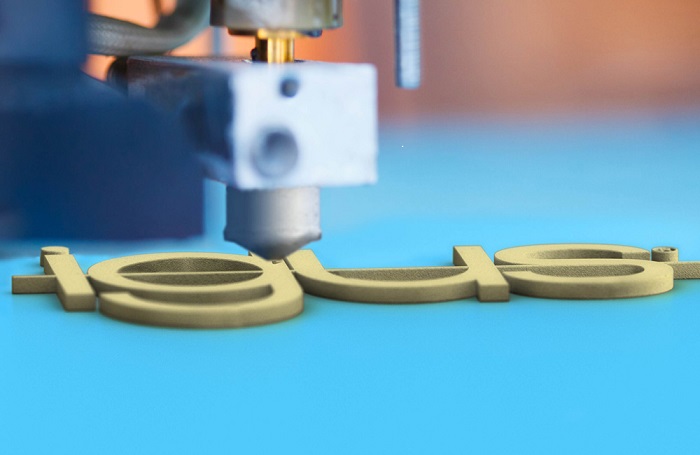
With 3D printing, it is easier to create more complex components due to the technology used in this method. In the same way, small intricate parts are also more easily created through 3D printing techniques than when they are moulded.
Verdict
If you take all of this into account, 3D printing looks like it could be the most cost-effective method – even with quantities up in the four-digit range. However, the range of materials for 3D printing is not as vast as the P2M option so, if you want pre-production parts or medium volume components, you should consider all the factors before making a decision: the cost saving, the material options, lead time and added value as a combination. Surely based on this, the P2M option outweighs the other options?
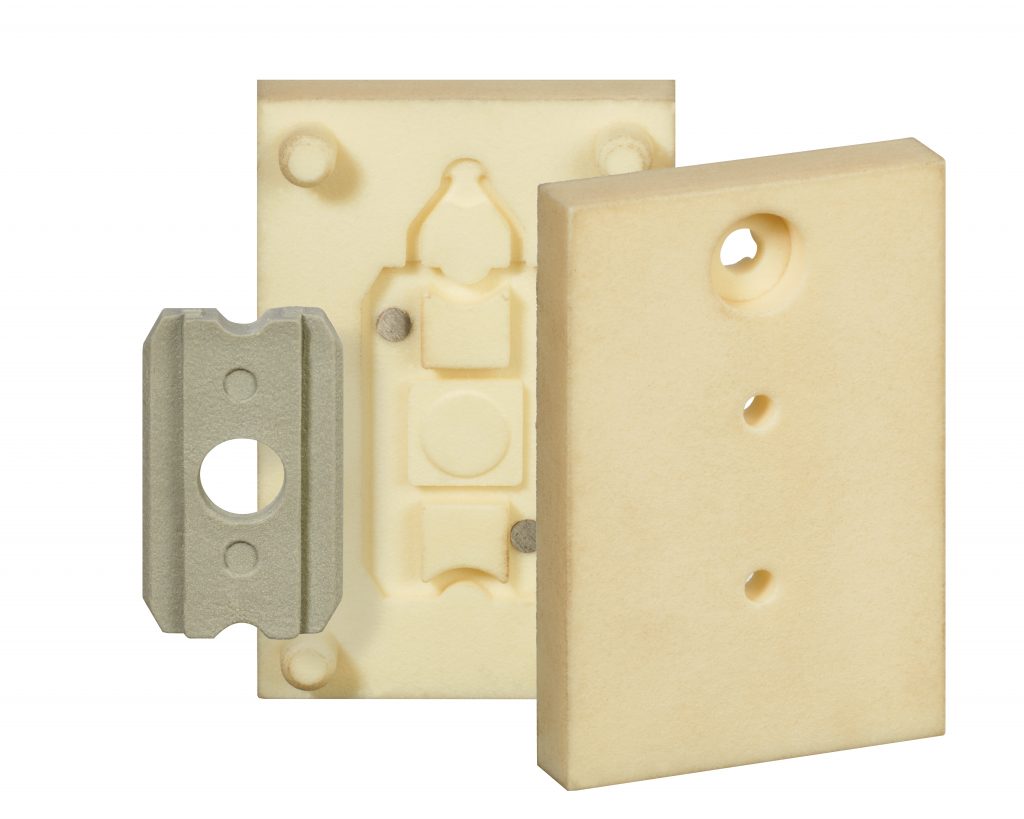

In my opinion, there is an argument for each type of manufacturing process.
However the flexibility you have with the P2M approach; the large variety of materials, being able to produce the parts in the igus® tribological materials, fast turnaround for parts and cost-effectiveness is a hard option to ignore when considering specific manufacturing processes.
Adapting known injection moulding approaches and merging them with innovative methods, igus® has created the perfect blend.

Visit the P2M page to find out more about the above products at igus®
Alternatively, contact the product manager Dean Aylott: daylott@igus.co.uk for any enquires.



