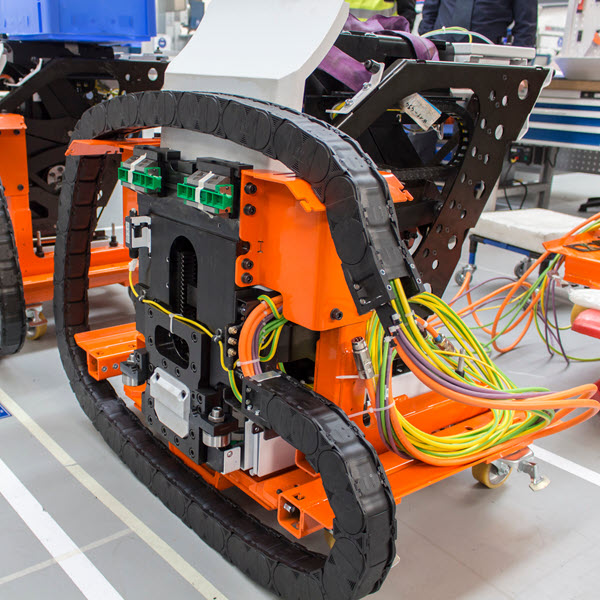
Long travel path – how do I find the right cable?
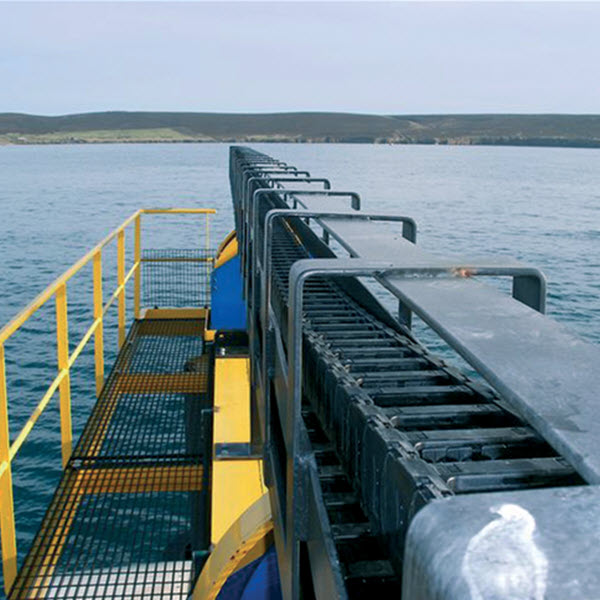
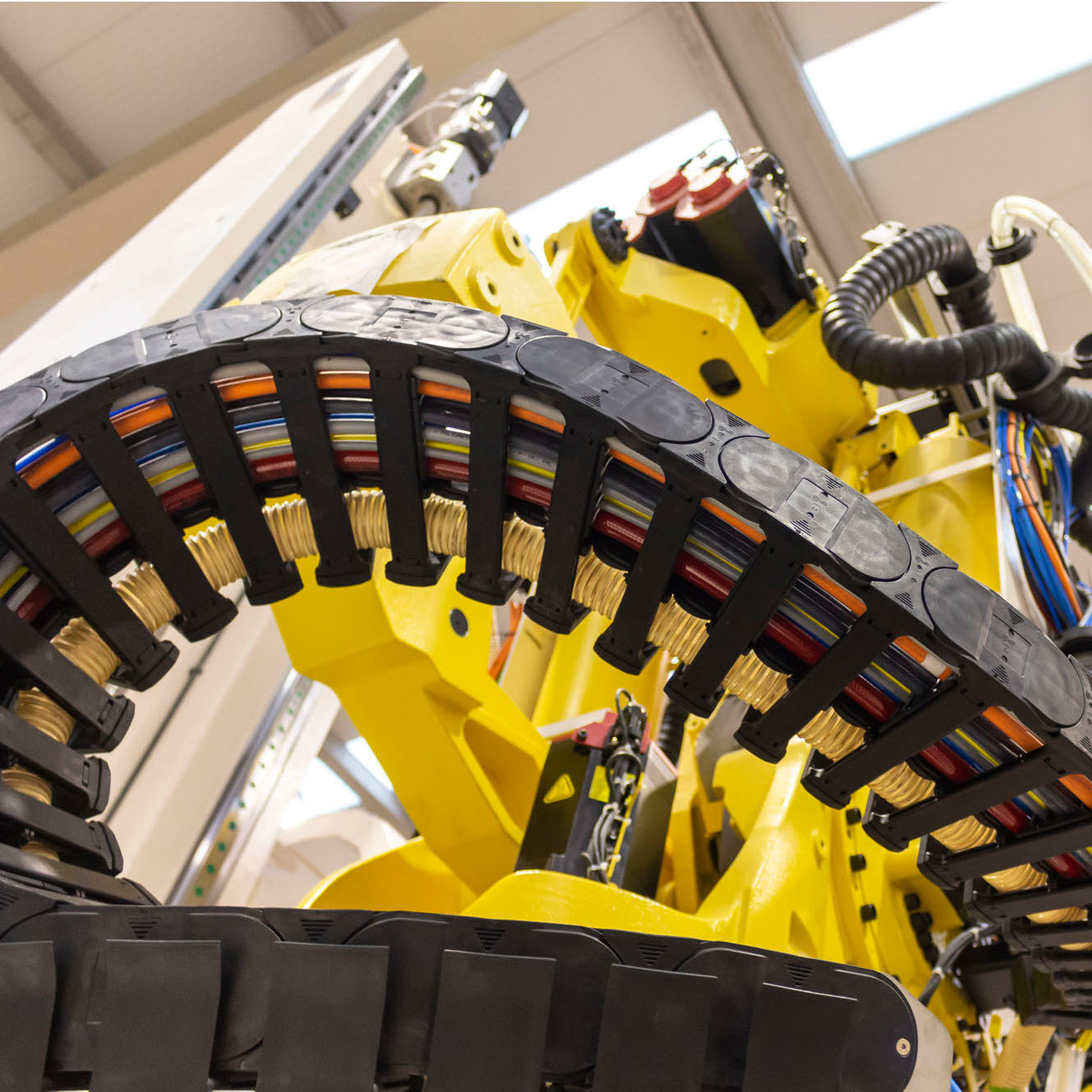
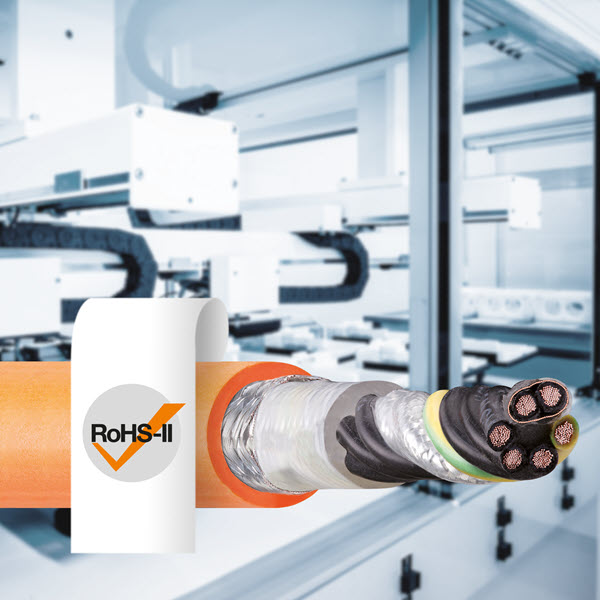
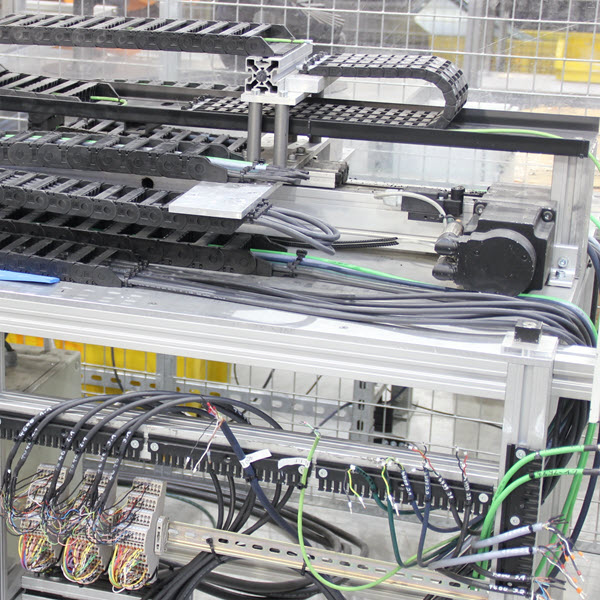
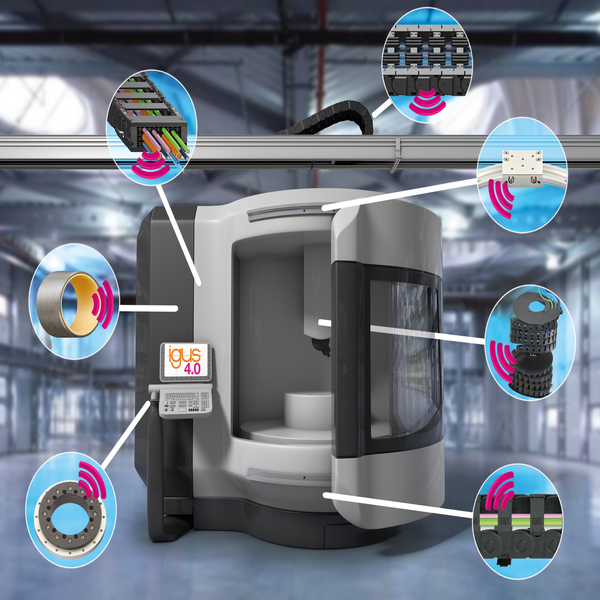
Long travel distances place high demands on the cable used and its durability. In today’s post, we cover what these are and how we can find out whether our management meets these requirements.
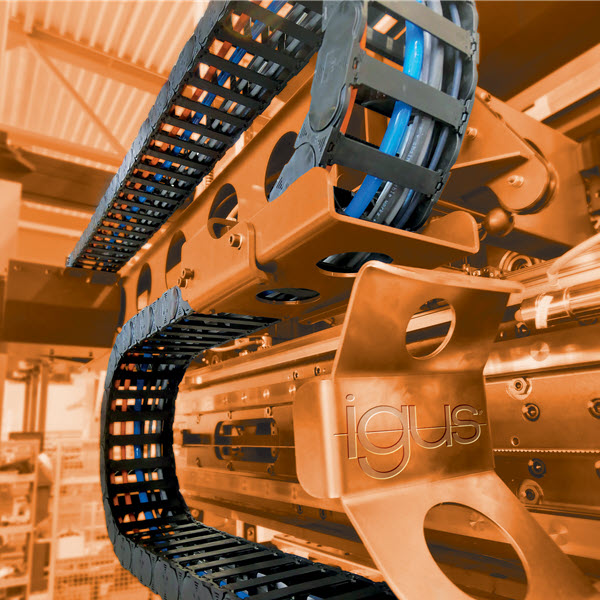
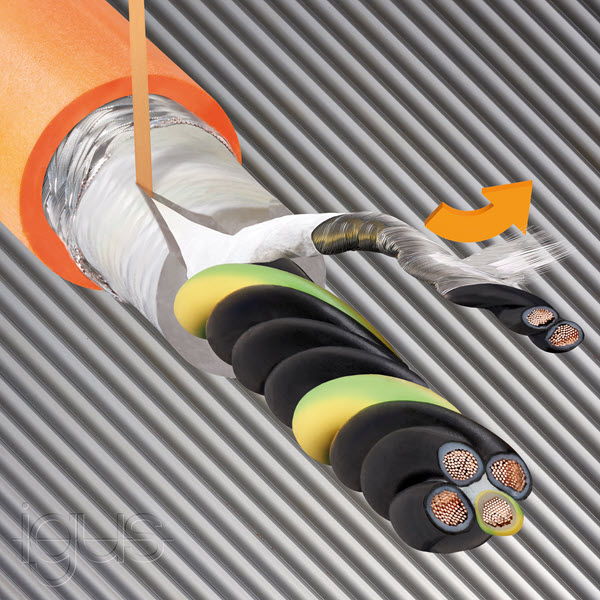
Durability, line structure, inner composition, and suitability are crucial points to take into account when selecting the right cable for your application.